Advanced Data Acquisition:
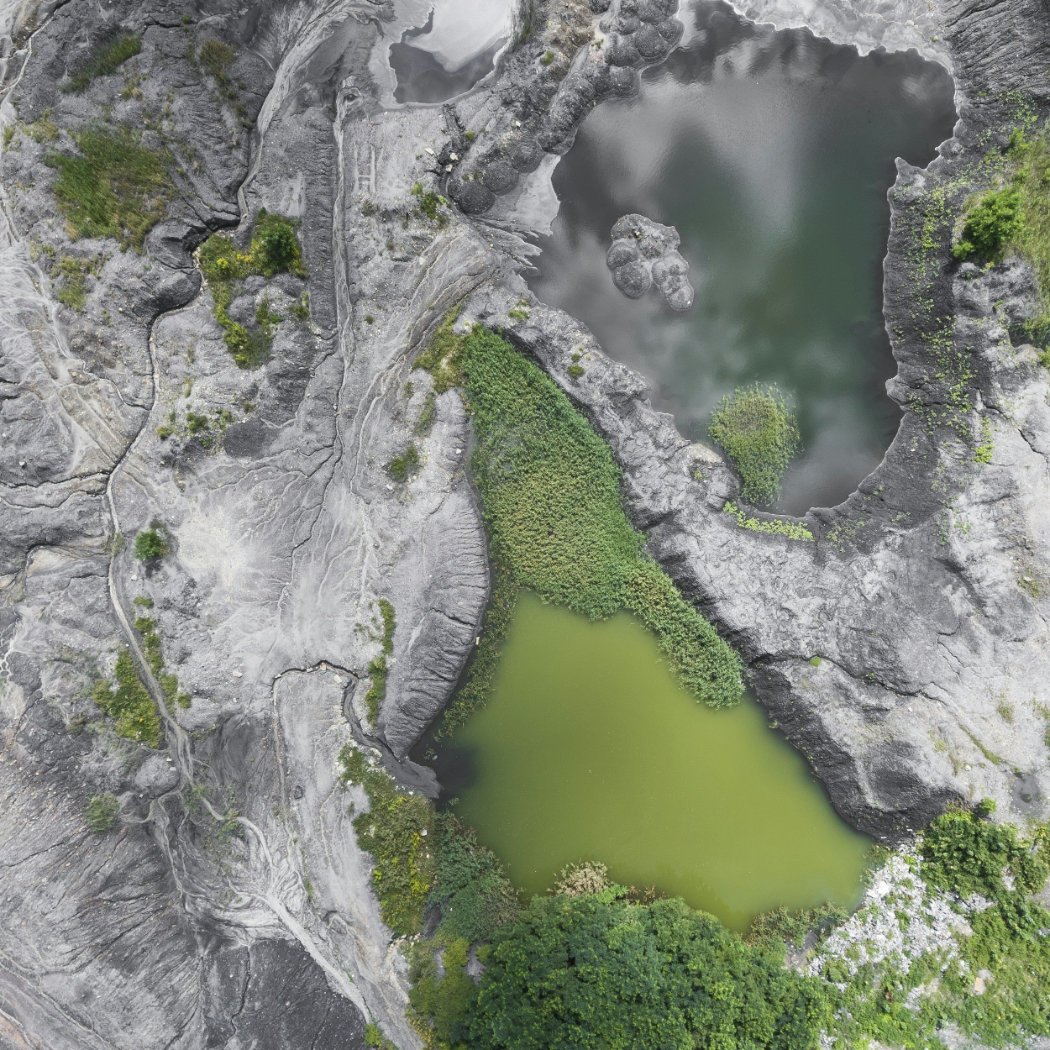
Aerial Survey
Aerial LiDAR and high-resolution photogrammetry, mounted on drones or aircraft, provide highly accurate topographic data for large-scale projects. Capture every detail of your site with precision mapping technology, ensuring the most accurate designs from start to finish.
Service Benefits:
High-Resolution Mapping: Capture detailed 3D models with sub-centimeter precision.
Fast Data Collection: Survey over 1000 acres in a single hour.
Versatile Applications: Ideal for mapping, construction planning, and environmental assessments.
Reduced Risk: Eliminate manual surveying in dangerous locations.
Comprehensive Data: Create before-and-after comparisons to enhance accuracy.
What You Can Expect
We begin by assessing your project’s goals and selecting the appropriate technology. Once the aerial survey is conducted, we process the data into precise 3D models and topographic maps. These deliverables are integrated into your project plans for accurate design and decision-making. Our team works closely with you throughout the process to ensure actionable insights are available at every stage.
Highlights of Design Projects We Support:
Mining: Surveying existing and new mine sites.
Environmental: Assessing vegetation and runoff.
Transportation: Evaluating new and existing construction.
Construction: Mapping large sites and corridors.
Agriculture: Surveying crop health and water usage.
Frequently Asked Questions
-
Aerial LiDAR is a remote sensing technology that uses laser pulses from aircraft or drones to capture detailed 3D maps of terrain and structures. The laser reflects off surfaces, allowing for accurate distance calculations to create topographic data.
-
Aerial LiDAR is commonly used for topographic mapping, infrastructure planning, flood risk assessments, forestry, and urban development. It’s ideal for large-scale projects where ground-based surveying would be inefficient.
-
Aerial LiDAR is highly accurate, typically achieving vertical precision within a few centimeters. It’s particularly suited for large-scale terrain mapping, though terrestrial LiDAR offers greater accuracy for smaller, detailed projects.
-
Aerial LiDAR covers large areas quickly, reaches difficult or dangerous locations, and generates high-resolution 3D models. It can also penetrate vegetation, making it effective for ground mapping in forested regions.
-
Aerial LiDAR is used to create digital elevation models, monitor erosion, assess flood risks, and support habitat mapping. It also helps identify geohazards like landslides, making it a powerful tool for environmental analysis.


